Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), also known as hexahydrocannabinol, is a cyclic hydrocarbon compound composed of six carbon atoms.
Its unique structure and chemical properties have sparked significant interest in various industries and scientific research.
With applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and chemical engineering, the extraction and synthesis of HHC are essential for obtaining pure and controlled quantities of this compound.
Table of Contents
What is HHC
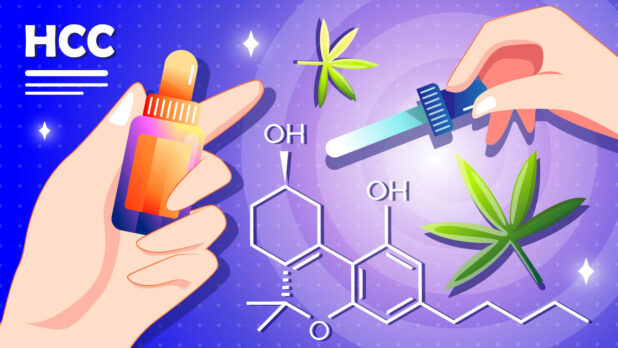
HHC, Hexahydrocannabinol, is a cyclic hydrocarbon compound with the molecular formula C6H10. It belongs to the class of cycloalkanes and shares similarities with other cannabinoids derived from the Cannabis plant.
Unlike its more well-known counterpart, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), HHC has a cyclohexyl ring structure instead of a benzene ring.
This difference in structure imparts distinct properties to HHC, making it a valuable compound for various applications. Explore a selection of HHC dabs for sale online.
Importance of HHC Extraction and Synthesis

The extraction and synthesis of HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) play a crucial role in advancing research and applications in different fields.
By obtaining HHC through extraction from natural sources or laboratory synthesis, researchers and manufacturers can access a pure and controlled form of this compound.
This allows for in-depth studies of its properties and potential applications in medicine, materials science, and catalysis.
Extraction Methods for HHC
Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction involves using a suitable solvent to selectively dissolve HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) from the mixture.
The choice of solvent depends on factors such as solubility, selectivity, and environmental impact. Solvents like hexane, toluene, or chloroform are often employed to extract HHC efficiently.
Supercritical Fluid Extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction utilizes supercritical fluids, which are substances that are above their critical temperature and pressure. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a commonly used supercritical fluid for HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) extraction. It offers advantages like low toxicity, easy removal, and recyclability.
Steam Distillation
Steam distillation involves the use of steam to volatilize HHC (Hexahydrocannabinol) from the mixture. The vapor is then condensed and collected separately. Steam distillation is particularly useful when working with plant material or complex mixtures containing HHC
Synthesis Process of HHC

Apart from extraction, HHC can also be synthesized in laboratories using various chemical reactions. Synthesis allows researchers to obtain HHC in controlled quantities and study its properties in detail. Two commonly used methods for synthesizing HHC are:
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Catalytic hydrogenation is a widely employed method for HHC synthesis. It involves the reaction of cyclohexene, a precursor compound, with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst, typically a transition metal such as palladium or platinum.
The reaction proceeds under specific temperature and pressure conditions, leading to the formation of HHC.
Chemical Reaction Pathways
Several chemical reaction pathways can be utilized for HHC synthesis. These pathways involve the stepwise conversion of precursor compounds into HHC through carefully designed reactions. The choice of pathway depends on factors such as reactant availability, reaction efficiency, and desired yield.
Factors Affecting Extraction and Synthesis
The extraction and synthesis of HHC are influenced by various factors that affect the efficiency, yield, and purity of the final product. Some significant factors include:
Temperature and Pressure
Both extraction and synthesis processes are temperature and pressure-dependent. Optimal conditions must be maintained to ensure efficient extraction of HHC or successful synthesis.
These parameters can affect reaction kinetics, equilibrium, and overall yield.
Catalyst Selection
In the case of synthesis, catalyst selection is crucial. Different catalysts can exhibit varying levels of activity and selectivity, directly impacting the conversion and yield of HHC. Researchers carefully choose catalysts based on their desired reaction outcomes.
Reactant Concentration
The concentration of reactants influences the extraction efficiency and synthesis yield. Balancing reactant concentrations ensures a favorable reaction environment and helps avoid unwanted side reactions or byproducts.
Challenges and Future Prospects

Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) finds applications across multiple industries due to its unique properties and versatile nature. Some notable applications include:
- Pharmaceutical Research: HHC’s interaction with the endocannabinoid system makes it an interesting target for drug development. It can serve as a basis for designing novel compounds with potential therapeutic effects, such as pain relief, anti-inflammatory properties, and antiemetic effects.
- Medical Treatments: HHC has shown promise as a pharmaceutical agent in the treatment of various medical conditions, including chronic pain, multiple sclerosis, and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
- Cosmetics and Skincare: The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of HHC make it a valuable ingredient in cosmetic and skincare products. It can help soothe skin conditions like eczema and reduce oxidative stress.
- Food and Beverages: Some manufacturers are exploring the use of HHC in food and beverages. It could potentially enhance certain flavor profiles and provide relaxation effects in certain formulations.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the extraction and synthesis of HHC have made significant progress, challenges remain. Improving extraction efficiency, exploring alternative synthesis methods, and ensuring compliance with legal regulations regarding THC content are ongoing research areas.
Additionally, more research is needed to fully understand the potential therapeutic effects and safety profile of HHC.
However, the future prospects for HHC utilization remain promising, with potential advancements in various industries. As the legal and regulatory landscape around cannabis-derived compounds evolves, more opportunities for research and development of HHC-based products are likely to emerge.
FAQ
What is the full form of HHC?
HHC stands for Hexahydrocannabinol.
Can HHC be synthesized in a laboratory?
Yes, Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) can be synthesized in a laboratory using various chemical reactions and processes, typically derived from cannabidiol (CBD) found in cannabis plants.
Are there any environmental concerns associated with HHC extraction?
The extraction of HHC from cannabis plants can have environmental concerns, especially if not carried out responsibly.
The use of harmful chemicals, improper waste disposal, and high energy consumption in the extraction process can impact the environment. However, there is ongoing research to develop more sustainable extraction methods for cannabinoids like HHC.
What are the main applications of HHC?
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) has various applications, primarily in the pharmaceutical and medical industries. It is being studied for its potential therapeutic properties and medical benefits, much like other cannabinoids found in cannabis.
Researchers are exploring its use in the treatment of pain, inflammation, anxiety, and other medical conditions.
How does the extraction and synthesis process of HHC contribute to sustainability?
Efforts are being made to improve the sustainability of HHC extraction and synthesis processes.
By using environmentally friendly extraction methods, reducing chemical waste, and optimizing energy consumption, researchers and manufacturers can ensure that the production of HHC has a minimal negative impact on the environment.
This supports the overall sustainability goals in the cannabis industry and promotes responsible practices for cannabinoid extraction.
Conclusion

The extraction and synthesis process of HHC is crucial for obtaining this versatile compound in pure form and desired quantities.
Through various extraction methods and synthesis pathways, researchers and manufacturers can access HHC’s unique properties for diverse applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and catalysis.
With ongoing research and development, the future holds immense potential for further discoveries and advancements in HHC-related fields.
 World Magazine 2024
World Magazine 2024